Depression is one of the most common mental illnesses worldwide: about 264 million people live with it. There are medication-based treatments out there, but they don’t work for everyone. Thankfully, though, there are alternatives available such as TMS and ECT treatments. When it comes to TMS vs ECT, what are the key differences when treating depression? Let’s find out.
Understanding Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Click Here to Learn More
What is TMS?
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate the nerves in your brain. This therapy uses magnetic pulses targeting certain areas of the brain, typically towards the front part of the brain called the prefrontal cortex. Worth noting: the TMS procedure does not require anesthetics or other medication.
TMS treatment sessions may happen up to 5 times per week, depending on the doctor’s recommendation. This happens for several weeks (4-6 weeks depending on the patient’s response) and can last anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour. No recovery time is necessary after the procedure, so you can resume your normal regular activities immediately following.
Side Effects of TMS
Some people have reported mild symptoms with this procedure including
- Face tightening,
- Tingling in the face, jaw, or scalp,
- Lightheadedness
- Mild headache
- Temporary hearing problems
- Small risk of seizures
What is ECT?
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is when electrical pulses are sent through areas of the brain to induce a brief seizure in the brain providing rapid improvements in the symptoms of mental health illness. Unlike TMS, ECT is usually performed under general anesthesia which means you are asleep during the procedure. ECT is complex and invasive, so when the patient is sedated, a team of medical professionals must be present. ECT is typically the last resort when other treatments fail to alleviate the symptoms of depression.
Usually, ECT treatment lasts about an hour: the procedure itself is about 10 to 20 minutes, with the remaining time left for patient recovery. Most patients need to rest for at least a day after a treatment session. Patients can receive ECT 2-3 times a week for 2-4 weeks.
Possible Side Effects with ECT
Side effects of ECT are uncommon and mild, they can include
- Confusion shortly after treatment
- Headaches or muscle aches
- Nausea
- Short-term or long-term memory loss
- Irregular heart rate (very rare)
TMS vs ECT: Summary of the Key Differences
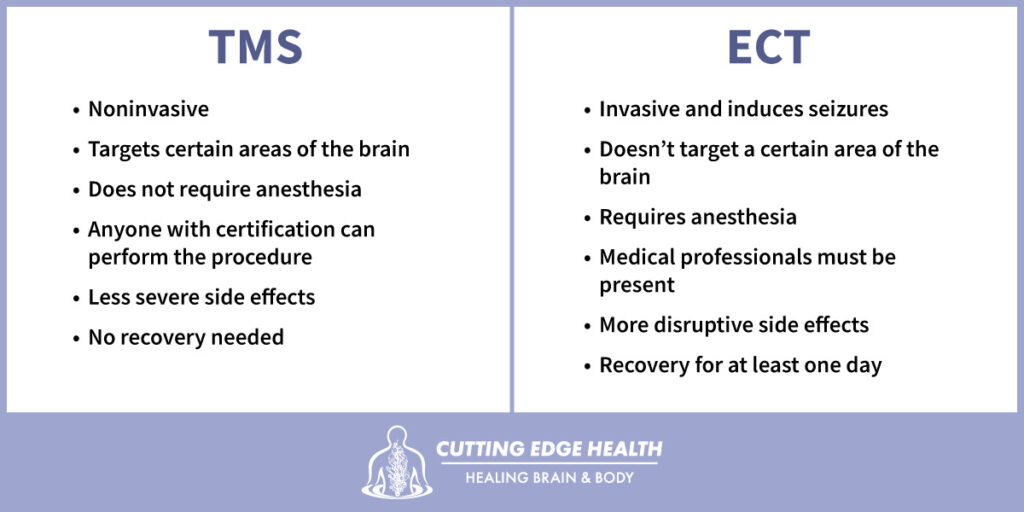
Though doctors use both TMS and ECT to treat depression, ECT is used when necessary to treat severe and potentially life-threatening depression. TMS is usually a safer treatment because it doesn’t require the use of anesthesia and sedation, is noninvasive, and has minimal side effects. For these reasons, many patients prefer TMS treatment over ECT treatment to address their mental health problems. If you’re one of those patients, Dr. Landrum at Cutting Edge Health provides TMS services to patients. Contact us and schedule your appointment so we can get you back the life you deserve.


